Faced with the challenge of rising U.S. government spending, the United States established the Department of Government Efficiency headed by Musk, aiming to achieve the goal of "streamlining the government, cutting spending, and restructuring federal agencies."
In response to this, Benioff, co-founder and CEO of CRM giant Salesforce, came up with an idea: using AI Agent, an autonomous intelligent system that can perform specific tasks without human intervention, can completely change government operations and automate reporting, auditing, case management and direct services to citizens, saving billions of dollars and eliminating delays.
This is just one application of AI Agent. With the rapid development of AI technology, AI Agent has made breakthroughs in the fields of AI chatbots, AI assistants, etc., and has gradually become the new favorite in the field of generative AI.
Bill Gates once predicted that AI Agent will be the next platform after large models (LLM). In the competition of large models, if the first half of the competition is about the basic capabilities of large models, then the implementation of AI Agent in the second half will become the most important form of application competition.
There are millions of small and medium-sized enterprises in the world. In the future, they can all let AI agents perform functions such as customer support and sales. For this reason, Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg said that there may be more AI agents in the world than humans.
1. Every company will have more than one AI Agent
A fundamental application of LLM is AI chatbots. It uses generative AI (GenAI) to provide responses based on a single interaction. A person asks a question and the chatbot responds using natural language processing.
The next frontier of GenAI is AI Agent, also known as Agentic AI or AI agent, which uses complex reasoning and iterative planning to autonomously solve complex multi-step problems, improve productivity and operational efficiency in various industries, and reduce costs.
AI Agent is the next revolution in AI. Zuckerberg said that every company, just like they have email addresses, websites and social media today, will have different AI Agents to perform different tasks. Everyone can have an AI Agent built into their phone. Every employee in an organization can have their own AI Agent to perform daily tasks.
"We are now entering a new era of autonomous AI agents that can take actions on their own and augment human work." Salesforce CEO Benioff called AI Agents the new "agency era," "as exciting as the cloud revolution, and fundamentally redefines the way humans work, live, and connect with each other."
A recent McKinsey report calls AI Agents “the next frontier of generative AI.” While versions of standalone software systems have existed for years, the natural language capabilities of generative AI reveal new possibilities, enabling systems to plan actions, use online tools to accomplish tasks that standalone software could, collaborate with other agents and humans, and further improve efficiency through learning.
So, what exactly is an AI agent? Tech giants and startups are exploring the potential of AI agents. However, some companies confuse AI assistants and AI chatbots with fully developed autonomous AI agents.
AI Agents consist of a set of instructions and AI models, as well as tools that can be used. Through these instructions, tools, and AI models, AI Agents can focus the power of AI models on specific tasks and provide the right information needed to achieve better results.
Among them, instructions usually refer to the role of the agent, such as the company's customer service, the tasks that need to be performed, and the way to perform the tasks. Then, through the dialogue, it is clarified which agent can help them, the waiting time of the agent is checked, and finally the specific request is transferred to the agent.
Tools enable agents to perform tasks, such as snippets of code that can be run to obtain information from other systems (even other AI agents or humans).
An AI model can be any model that can understand and apply instructions and use tools.
At present, the application scenarios of AI Agents in enterprises are constantly expanding. The potential application areas of AI Agents are very broad, limited only by creativity and expertise. From simple tasks such as generating and distributing content to more complex scenarios such as orchestrating enterprise software, AI Agents are changing various industries.
Common application scenarios include customer service, reducing response time and improving satisfaction; content creation, quickly creating high-quality, personalized marketing content; daily office work, such as scheduling, extracting meeting minutes, and distributing them; HR services, such as onboarding services, consulting services, etc.; software engineering, improving developer productivity by automating repetitive coding tasks; healthcare, extracting key information to help doctors make more informed care decisions, and automating administrative tasks and recording clinical notes in patient appointments to reduce the burden of time-consuming tasks.
AI is driving a new wave of automation, moving from robotic process automation (RPA) to more sophisticated automated AI agents. At the same time, automation companies that once dominated with RPA solutions are now adopting agent-based systems. The RPA era is centered on creating software robots to handle repetitive, rule-based tasks. These robots have become the basis of many corporate automation strategies, automating tasks that can be broken down into deterministic decisions, that is, decisions with a certain outcome.
In response, automation platforms are adopting AI agents to enable greater flexibility. Unlike robots, agents can manage probabilistic decisions, meaning they can adapt to and learn from a variety of outcomes in real time. This dynamic capability enables agents to move beyond simple automation and begin acting as collaborators in the workflow.
AI Agents provide dynamic, adaptable workflows that can manage structured and unstructured decision-making processes. While robots continue to handle rule-based tasks, AI Agents are stepping in to manage more complex probabilistic decisions, thereby improving operational efficiency. In the future, industry leaders are increasingly paying attention to multimodal AI systems that balance human-machine collaboration, ushering in an era of change in enterprise workflows.
2. Big model companies build AI Agent moats
In the era of generative AI, every enterprise is trying to build its own AI application to enable enterprises to improve business capabilities, increase profit expectations, and improve production efficiency. However, enterprises face many challenges from algorithm technology, data quality, data privacy, computing efficiency and cost.
More and more large model companies and technology companies have begun to deploy AI Agents to help companies solve the above challenges. LLM companies and cloud service providers have taken the lead and have a clear advantage in AI Agents.
Alibaba launched the AI Agent framework Qwen Agent, which can build various AI agents that can perform complex tasks. Qwen Agent is a framework for developing LLM applications based on the instruction following, tool use, planning and memory functions of Qwen 2.0. Alibaba has open-sourced this framework, and it also comes with sample applications such as browser assistants, code interpreters and custom assistants.
Qwen-Agent has the ability to follow instructions, use tools, plan and remember. Users can use it to build various AI agents that can perform complex tasks, call tools such as calculators, search engines, etc., process long documents, etc., and call applications such as browser assistants, code interpreters, and custom assistants.
In terms of accessibility, users can use Alibaba Cloud DashScope's model service or use the open source Qwen model to deploy and manage their own model services.
Another tech giant, Tencent Cloud, launched a one-stop intelligent agent development platform, Tencent Yuanqi, to help users create and manage various AI agents. Tencent Yuanqi allows users to build, publish and deploy intelligent agents, or AI Agents, through simple operations, and supports publishing these agents to multiple channels, such as QQ, WeChat customer service, WeChat mini-programs, and WeChat public accounts.
This platform integrates four major functional modules: prompt words, plug-ins, knowledge base and workflow. The prompt word module allows users to fine-tune the behavior patterns and response methods of the intelligent agent; the plug-in module provides a variety of plug-ins including web page parsing and image understanding, and supports user-defined plug-ins to meet a wider range of needs; the knowledge base module supports the import of knowledge files in various formats to enhance the knowledge reserve capacity of the intelligent agent; and the workflow module, as a low-code editing tool, enables users to flexibly arrange the working order of plug-ins, knowledge bases and large model nodes, thereby achieving precise control of task logic.
The underlying large model capability of Tencent Yuanqi comes from its Hunyuan large model. In addition, the Tencent Yuanqi platform actively promotes community building, encourages users to participate in the creation and release of the plug-in ecosystem, and jointly promotes the development of the platform ecosystem.
The latest achievements of Zhipu AI in AI Agent are particularly eye-catching. Zhang Peng, CEO of Zhipu AI, announced that its autonomous task completion agent AutoGLM has been upgraded again, supporting autonomous execution of long-step operations of more than 54 steps, and can also execute tasks across apps.
Zhipu AI demonstrated its latest achievements in AI Agent and released three intelligent agents that use AI to replace humans in performing tasks, namely Phone use for mobile phones - AutoGLM, Compute use for computers - GLM PC, and GLM-Web capabilities for web pages.
Among them, the PC-based autonomous agent, GLM-PC, is undergoing internal testing for scenarios such as meeting reservations, document processing, web page searches, and remote command sending.
As the world's largest cloud service provider, AWS has launched Multi-Agent Orchestrator, which provides solutions for managing multiple AI agents and handling complex conversations. The framework routes queries to the most appropriate agent, maintains conversation context, and integrates with various environments, including serverless computing power AWS Lambda, local settings, and other cloud platforms.
Its orchestrator supports Python and TypeScript, supports dual-language implementation, allows streaming and non-streaming responses from agents, and includes pre-built options for rapid deployment. In addition, it also provides a wide range of features such as intelligent intent classification, context management, and extensible integration of new agents.
AWS also highlighted the capabilities of six specialized agents it has on GitHub, including agents for travel, weather, math, and health. The orchestrator switches between agents to manage multi-turn conversations and various tasks while preserving context.
Similarly, IBM has also launched an open source toolkit Bee Agent Framework for creating and deploying agent-based workflows at scale. Currently, Bee Agent is in the Alpha testing phase, supports various AI models, and provides compatibility with IBM Granite and open source Llama 3.2 models.
NVIDIA, a leader in AI computing power, did not miss this opportunity. In August 2024, NVIDIA released the NVIDIA NIM Agent Blueprint, a reference workflow for standardized generative AI use cases, to help enterprises and developers solve AI Agent management problems.
NIM Agent Blueprint includes partner microservices, one or more AI Agents, reference code, customization documentation, and Helm charts for deployment. With NIM Agent Blueprint, developers can quickly start creating AI applications that use one or more AI agents, including sample applications built using NVIDIA NeMo, NVIDIA NIM, and partner microservices.
Enterprises can modify NIM Agent Blueprint with their own business data and run their generative AI applications in accelerated data centers and clouds. With NIM Agent Blueprint, enterprises can continuously improve their AI applications based on user feedback, forming a data-driven AI flywheel.
NVIDIA partners including Accenture are helping enterprises use AI Agents through solutions built with NIM Agent Blueprints. The Ottawa Hospital in Canada uses NVIDIA AI-powered Deloitte Frontline AI Teammate to deploy an AI assistant to provide a better patient experience and reduce administrative burden.
Built using NVIDIA AI Enterprise and Deloitte’s conversational AI framework, Deloitte’s Frontline AI Teammate enables human-machine interaction in healthcare environments. Deloitte’s lifelike avatars, developed on the NVIDIA Omniverse platform, can answer complex healthcare questions that are critical in healthcare delivery.
3. Enterprise service giant launches AI Agent
Across industries and job functions, generative AI is transforming organizations by turning vast amounts of data into actionable knowledge, helping employees work more efficiently and effectively.
At present, AI Agents launched by different companies are gradually covering various fields such as corporate office, finance, HR, customer service management, and IT service management.
Oracle launches 50+ AI Agents to automate tasks in finance, HR and other fields. Oracle announced that it will integrate more than 50 professional AI Agents into its Oracle Fusion Applications Suite in 2024. AI Agents will automate routine tasks in key areas such as finance, human resources, supply chain, sales, marketing and customer service, allowing employees to focus on more strategic initiatives.
New AI Agents powered by generative AI are designed to automate end-to-end business processes and provide personalized insights and recommendations. For example, in the human resources field, the "Shift Scheduling Assistant" helps manage employee shifts while ensuring regulatory compliance, while in the finance field, the "Advanced Forecasting Agent" uses AI models to generate accurate revenue forecasts.
In addition, Oracle Fusion Applications Suite supports enterprises to standardize operations and break down silos by managing multiple business processes on a single cloud platform. This continuous innovation is updated regularly to help organizations adapt to changing business needs.
SaaS leader Salesforce has launched Agentforce, a low-code/no-code platform for building autonomous AI agents that enables companies to create, customize and deploy AI-driven autonomous agents to support the work of customers and employees.
Agentforce not only uses low-code tools to allow users to easily create agents, but also claims that "Agentforce is in every application", integrating this technology into multiple cloud platforms such as Sales, Service, and Marketing, covering a wide range of usage scenarios.
This wide range of applicability and powerful intelligence capabilities make Agentforce far superior to traditional AI tools in terms of user experience and data personalization. It is said that Salesforce customers already have about 200 million AI Agents in the trial stage. The number of AI Agents may reach the 1 billion mark in just two years.
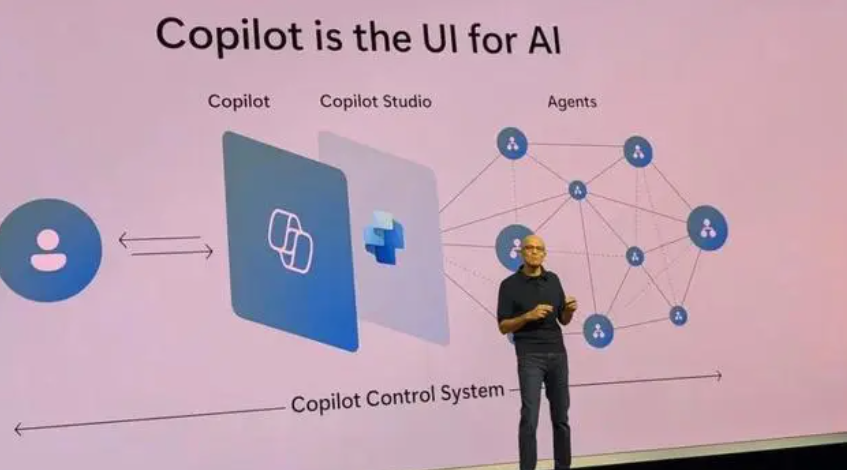
Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft, the world’s largest software company: “Copilot is the UI of AI”, ideally, every employee will have a Copilot that understands them, understands their work, helps them be more productive, enhances their work and saves time.
Microsoft's Copilot was first announced at the Ignite conference in late 2023, and the Copilot agent was launched in 2024 and integrated into the Microsoft 365 ecosystem.
The tech giant has introduced AI Agents across its multiple platforms, including SharePoint agents that help users gain insights from specific content, employee self-service agents for HR and IT tasks, and Facilitator agents for efficient collaboration and note-taking in Teams meetings. There is also a new Project Manager agent in Planner that can handle everything from plan creation to task execution.
Users can also customize agents, name them and define behaviors to meet specific business needs. Microsoft's Copilot Studio will allow users to create agents that automate specific business processes, and IT departments will have a platform to manage, protect and measure these systems.
Microsoft’s new Copilot Actions, now available in private preview, uses AI to automate repetitive tasks, including anything from automating meeting summaries and generating weekly reports to automating meeting preparation and handling other routine workflows.
In terms of security, Microsoft emphasizes its data confidentiality measures, such as Azure tenant boundaries and strict data protection protocols, to ensure the security of an organization's data.

ServiceNow, the king of HRM software, launched its own AI Agent in September 2024 - Now Platform, including ServiceNow AI Agents, which aims to improve the round-the-clock productivity of departments such as IT, customer service, human resources and procurement.
ServiceNow AI Agent uses advanced reasoning and builds on cross-enterprise data through the Now Platform to evolve from more familiar prompt-based activities to deep contextual understanding that engages people for strong oversight and governance.
The first ServiceNow AI Agents to be implemented include Customer Service Management (CSM) and IT Service Management (ITSM) AI Agents. In the future, using ServiceNow's multimodal AI, AI Agents will be able to extract context from inputs such as voice, video, and images, and provide personalized, relevant responses, ultimately driving 24/7 productivity at scale through hundreds of use cases in IT, customer service, procurement, human resources, software development, and other fields.
By comparing AI Agents in the enterprise service field, we found several common features:
First, corresponding platforms or frameworks have been launched to complete the creation and management of AI Agents. Some platforms even have low-code/no-code functions to facilitate the creation of AI Agents.
Second, in terms of functionality, AI Agents currently perform mostly repetitive and simple tasks due to different application areas, such as customer service, consulting services, and employee self-service. In the future, the application areas will be more numerous and more complex. Although Microsoft's Copilot covers a wide range, it is "chaotic" to ordinary people.
Third, in terms of ease of use, Salesforce uses low-code/no-code, ServiceNow's Now Learning and Now Assist Skills Kit, etc., all provide rich learning and development support, while Microsoft has launched simplified tools to facilitate use by users at all levels.
Fourth, in terms of big model support, different companies support their own big models or open source big models. In the future, when companies create AI Agents, the selection and fine-tuning of big models will be particularly critical.
Finally, in terms of security and trust, protecting user data is key. At present, data security is the focus of every platform, and different companies attach great importance to data security, otherwise there will be chaos.
4. Dawn is just around the corner
The application prospects of AI Agent are promising. According to the Research and Market report, the AI Agent market is expected to grow from US$5.1 billion in 2024 to US$47.1 billion in 2030, with a compound annual growth rate of 44.8% from 2024 to 2030.
Software framework LangChain recently released a survey report, in which 51% of respondents said they were already using AI Agents in production, 63% of medium-sized companies had deployed agents in production, and 78% of companies had plans to integrate AI Agents.
AI Agents will develop in the direction of interpersonal collaboration, multimodality, multiple AI Agents, and embodied intelligence. In the future, AI Agents will no longer be just programs that execute simple commands, but will have deeper understanding and reasoning capabilities, and will be able to communicate more naturally and deeply with employees in the enterprise. AI Agents will learn to use external tools to obtain the required information, and even be able to self-reflect and learn to optimize their own behavior and decision-making.
Human-machine collaboration is becoming the new norm for AI Agents. This collaborative model will allow humans and AI to participate in the workflow together, with AI providing suggestions and assisting humans in completing their work, but at this point it will still appear more as a tool. AI Agents will also develop in the direction of more personality traits and emotion recognition capabilities to provide a more natural and personalized interactive experience.
With the development of multimodal fusion technology, AI Agent can better understand and respond to employees' instructions. Just like humans, it can listen, read, see and feel. This will enable AI Agent to be applied to a wider range of fields, such as medical diagnosis, autonomous driving, smart security, etc.
In the future, AI agents will also develop from "working alone" to "working as a team", and will be able to simulate complex work and decision-making processes. Just like the cooperation between people, in a multi-agent system (MAS), each agent has its own responsibilities and tasks.
There are still many process, security, and other challenges that need to be addressed before the world can run AI agents.
Building trustworthy AI agent systems involves solving problems that never existed before. While the potential is huge, one of the biggest challenges remains data orchestration. Many companies are struggling with how to manage and coordinate data across platforms. Technology companies are actively working on solutions, focusing on building the right infrastructure to support AI agents and robots, ensuring that AI-driven automation can meet the needs of complex workflows.
Data security can never be overemphasized. Businesses and organizations will not pay for small language models or large language models, they will only pay for the results of the system, thus allowing the system to extract proprietary data and use it for competitive advantage, no matter what the system is. If data is leaked as a result, it will harm all parties.
If you think AI Agents will spread like a flood, then as an employee of a company, you should worry about being replaced by AI. How to manage these different AI Agents? In the future, a management AI Agent may be needed.